MMF_P1R44F-009 : Start Up manual
1. Informations
1.1 Release
 |
|||
| Document: | mmf_p1r44f-009 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Description: | Start up Manual p1r44f-009 | ||
| Editor: | Andrea Zarantonello | ||
| Approver: | Giuliano Tognon | ||
| Link: | https://www.qem.eu/doku/doku.php/strumenti/qmoveplus/c1r44/p1r44f-001/mmf_p1r44f-009 | ||
| Language: | English | ||
| Release document | Description | Note | Date |
| 01 | New manual | 30/11/2022 | |
1.2 Specifications
The copyright of this manual is reserved. No part of this document can be copied or reproduced in any form without the prior written permission of the QEM.
QEM has no assurances or guarantees on the content and specifically disclaims any liability inherent in the guarantees of eligibility for any particular purpose. The information in this document is subject to change without notice. QEM does not take any responsibility for any errors that may appear in this document.
Trademarks:
QEM® is a registered trademark.
2. Setting
2.1 General view machine
Machine view from above:

Machine view from right side:

| n: | Description: |
|---|---|
| 1 | Raw slab |
| 2 | Belt Encoder |
| 3 | Limit sensor bar |
| 4 | Center of the sensors / centre of the bridge axis travel |
| 5 | Bridge |
| 6 | Polishing heads |
| 7 | Belt direction |
| 8 | Orthogonal Offset |
2.2 Belt setting
Belt axis resolution

| PROCEDURE | |
|---|---|
| 1 | Make a mark on the belt and a corresponding mark on the fixed part |
| 2 | Reset the ENCODER value with the  key key |
| 3 | Move the belt approximately 4000 mm |
| 4 | Read the value in the ENCODER parameter and set the PULSE parameter with the same value |
| 5 | Using a meter, measure the distance between the mark on the fixed part and the mark on the belt |
| 6 | Enter the measurement in the MEASURE field |
Belt calibration
Press  from axis resolution page to go to Belt calibration page.
from axis resolution page to go to Belt calibration page.

| Setup of the parameter OFFSET | |
|---|---|
| 1 | Press calibration button to activate the calibration. |
| 2 | Enter 0 (zero) in the parameter OUT VOLTAGE. |
| 3 | Adjust the parameter OFFSET (by direct entry, using the buttons  , ,  , or by the automatic procedure from the button , or by the automatic procedure from the button  ) so that the axis POSITION is not variable (or varies very slowly). ) so that the axis POSITION is not variable (or varies very slowly). |
| 4 | Press calibration button to disactivate the calibration. |
| Check count and direction of rotation: | ||
|---|---|---|
| control that an output voltage greater than 0 (zero) corresponds to an increasing variation in the axis position. | ||
| 1 | Press calibration button to activate the calibration. | |
| 2 | Enter a positive value in parameter VOUT. | |
| 3 | Check that the POSITION parameter increases. | |
| 4 | Press calibration button to disactivate the calibration | |
| 5 | ||
| Maximum speed: | |
|---|---|
| determine the axis movement speed that corresponds to a 10V output voltage. | |
| 1 | Press calibration button to activate the calibration. |
| 2 | Enter 1V value in the parameter VOUT |
| 3 | Read the value shown in parameter SPEED. |
| 4 | Determine the value of parameter MAX SPEED with the formula: SPEED x 10 |
| 5 | Press calibration button to disactivate the calibration |
| 6 | Enter the value calculated in MAX SPEED. |
2.3 Bridge Setting
Bridge Alignment with Sensor Bar
The bridge, to be aligned with the sensor bar, must have the 0 sensor aligned with the first slab detection sensor.
To have the 0 sensor and the first sensor of the bar perfectly aligned, it is recommended to use a laser indicator
Bridge resolution

| Procedure | |
|---|---|
| 1 | By pressing the “ - ” key, the instrument provides - 1 Volt |
| 2 | By pressing the “ + ” key the instrument provides + 1 Volt |
| 3 | Press the “ - ” key, bring the bridge axis towards an extreme (without touching the limit switch) |
| 4 | Make a mark on the mobile part, correspondingly make a mark on the fixed part |
| 5 | Reset the ENCODER value with the  . key. . key. |
| 6 | With the “ +” key move the axis towards the opposite extreme (without touching the limit switch) |
| 7 | Use a meter to measure the distance between the mark on the fixed part and the mark on the mobile part |
| 8 | Enter the measurement in the MEASURE |
| 9 | Copy the number of the ENCODER field to the PULSE |
Bridge calibration
Important :
Need to act on the parameters of inverter / Brushless Driver / servo valves
to eliminate the ramp (the ramps will be managed by the instrument)
Calibration
| 1 | Using the “BRIDGE RESOLUTION” page, bring the bridge axis to the center of its travel |
| 2 | reset with the key “ = 0 |
| 3 | go to the ” BRIDGE TUNING“ page |

| 4 | Disconnect the control leads (+/-10 Volt) Inverter/Driver/servo valves |
| 5 | Calibrate the Inverter/Driver/Servo Valves devices so that you have high sensitivity |
| 6 | Make a short circuit of the analog control inputs of the Inverter/Driver/Servo valve devices |
| 7 | Calibrate the OffSet of the Inverter/Driver/Servo valve device so that the bridge axis stays still (don't move) |
| 8 | Connect the analog control leads to the Inverter/Driver/Servo valve |
| 9 | Press the “A” key, the instrument will automatically calculate the OFFSET voltage |
| 10 | Move the bridge axis to 1/5 of the travel |
| 11 | Enter the value 1 V in the “VOLTAGE OUTPUT” field |
| 12 | Read the velocity |
| 13 | Multiply the velocity value by 10, then enter the result in the “maximum velocity” field |
Warning: If the automatic OffSet voltage calculation procedure (point 9) fails,
perform the following manual procedure:
To determine :
-
with which value of positive voltage the bridge moves forward
-
with which value of negative voltage the bridge moves back
then, set the offset voltage at the middle of these two values
Example :

Dynamic calibration
| 1 | Bring the bridge axis to 1/5 (20%) of the travel |
| 2 | Press the ” = 0“ key |
| 3 | Enter a value in the “DELTA” field, a value equal to 4/5 (80%) of the travel |
| 4 | Set INTEGRAL TIME = 0 |
| 5 | Set FEEDFORWARD = 0 |
| 6 | Set PROP.GAIN = 0.02 |
| 7 | Set ACC TIME = 3 |
| 8 | Set DEC TIME = 3 |
| 9 | Set MAX FOLL ERROR = 9999 |
| 10 | Set the speed value equal to 30% of the maximum speed |
| 11 | Press Start |
| 12 | The bridge will start to swing |
Do the following activities repeatedly and calmly. The goals are as follows:
-
speed as fast as possible
-
acceleration ramps as short as possible
-
low following error
Method:
| 1 | Increase the PROP.GAIN parameter slightly (example = 0.03 …0.04…0.05 …) |
| 2 | Observe if the following error is less than 30 mm |
| 3 | Then, decrease ACC TIME and DEC TIME a little bit |
| 4 | Increase the PROP.GAIN parameter slightly |
| 5 | Observe if the following error is less than 30 mm |
| 6 | Increase the speed from 30% to 40% |
| 7 | Increase the PROP.GAIN parameter slightly |
Repeat from 1 to 7 until the axis vibrates.
When the axis vibrates, set the PROP.GAIN to - 10 %

| Description | Parameter | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Positive Direction Acceleration | PB 08 |
| 2 | Constant speed | |
| 3 | Deceleration | PB 09 |
| 4 | Negative Direction Acceleration | PB 08 |
| 5 | Constant speed | |
| 6 | Deceleration | PB 09 |
| 7 | Pause | PB 10 |
Note: accelerations/decelerations with “S” ramps (parameter “PG 34” ) decrease the number of right-left cycles, but it helps to make the movement of the bridge more harmonious

Setting following error:

-
With the bridge moving, lower the following error value from 9999 to 100.
-
Then, progressively with small variations, decrease the value from 100 towards 0000.
-
Found the value that will trigger the alarm, add a 15%
Warning: The following error must be less than 30.

The button  reset max and min following errors
reset max and min following errors
2.4 Sensor setup
-
Align the sensor bar with the bridge: Alignment
-
position the sensors, so that the center of the bridge travel corresponds to the center of the sensors (see main image)
-
set the number (parameter PS01) and the type (parameter PS02) of sensors in the SENSORS page

-
set the parameter PG05:Orthogonal Step (distance of the sensors) and the parameter PG06:Horizontal Step (space determined by the encoder) in the generic SETUP page
| Slab Shape Detection Representation | ||
|---|---|---|
 | 1 | Slab |
| 2 | Limit Switches / Sensors | |
| 3 | Space determined by encoder (PG06) | |
| 4 | Distance of the sensors (PG05) | |
-
check the functionality of the slab detection sensors on the DIAGNOSTICS 2 page. If the limit switches detect the presence of the slab, the LEDs light up.
2.5 Head Setting
Interaxes
Set in INTERAXES TOOLS page, the distance (mm) of every polishing head (and brush) compared to the acquisition sensor bar (limit switches)


Heads parameters

-
Set diameter of the heads:
PT 01 ÷ 22
 The diameter of the head passes through the center of the tools
The diameter of the head passes through the center of the tools
The diameter of the heads is important because the descent and ascent of the heads takes place following the following criteria:
PG35: Head segmentation = 4
| 1 |  | The head is divided into 8 pieces |
| 2 |  | The head go down only if at least 5 of the 8 pieces see the marble slab under them |
| 3 |  | The head go up only if the pieces seeing the slab below go from 5 to 4 |
PG35: Head segmentation = 6
| 1 |  | La testa viene divisa in 8 parti |
| 2 |  | The head go down only if at least 7 of the 8 pieces see the marble slab under them |
| 3 |  | The head go up only if the pieces seeing the slab below go from 7 to 6 |
-
Set Orthogonal Offset, i.e. the distance between the working heads and the midline of the bridge: PT 23 ÷ 44
-
Set the Partial Ascent time: PT 45 ÷ 66
-
Set the Total Ascent Delay time: PT 68
| Solenoid valves “closed centres” heads up and down | Parametri: | |
|---|---|---|
 | Valve | |
 | cylinder down | |
 | Closed centers | PT 45 ÷ 66 |
 | cylinder up | PT 68 |
In order for the cylinder to descend quickly, its stroke is decreased.
During the ascent it is not allowed to ascend completely.
By setting the partial ascent time of the head (parameters 45 ÷ 66) the ascent output is de-energized after that time and, mechanically, when the ascent and descent are de-energized, the upper chamber is in communication with the lower chamber of the cylinder, locking it in that position (closed centers).
The total ascent will be done only when the head no longer has to work.
2.5.1 Set the heads up / down advance, in relation to the movement of the bridge.
Orthogonal correction
It is very important that the bridge is exactly in the position where it should be, otherwise the descent and ascent commands of the heads cannot be performed correctly.
So it's very important that the following error (difference between the virtual and real position) is the minimum possible
-
Remove the abrasives and make sure that the heads, going down, cannot damage the belt
-
Set the conveyor belt at a low speed
-
Set the bridge at maximum speed
 | The blue arrow indicates the slab entering in the polishing machine. P is the observation point, observe the behavior of the first head |
 | If the bridge goes slow the head goes down to point A and goes up to point B |
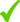    | If the bridge goes fast the ascent and descent commands must be anticipated (point L) so that the head descends shortly after the left edge and rises just before the right edge of the slab otherwise the first part of the slab would not be polished (point N) and the polishing tool would tilt, damaging the edges of the slab (point G) Important : set the advance of the descent very well |
 | Page where you need to act to anticipate / postpone the heads. In the parameter “reference speed” you need to insert the speed of the bridge. If you dont put a value in “reference speed”, the correction parameters are not adapted to each speed change of the bridge. |
2.5.2 Set the heads up / down advance, in relation to the movement of the belt.
Horizontal Correction
-
Remove the abrasives and make sure that the heads, going down, cannot damage the belt
-
Set the belt to maximum speed
 | The blue arrow indicates the observation point. The conveyor belt goes slowly, typically 3000 mm per minute so the advance space for the descent and ascent of the heads is “minimum” The red arrow indicates the direction of travel of the conveyor belt. |
 | As seen in the previous method, calibrate the up and down advance so that the heads work on the entire surface of the slab, taking care not to go beyond the edges. |
 | Page where you need to advance/postpone the heads In the parameter “reference speed” you need to insert the speed of the bridge. If you dont put a value in “reference speed”, the correction parameters are not adapted to each speed change of the bridge. After the correction set a low belt speed, then check if the head ascent and descent has remained correct |
3. Support
Request for assistance
In order to be able to provide you a quick service, at the minimum cost, we need your help.
 |  |
| Follow all the instructions provided in the manual MIMAT | If the problem persists, fill in the “Assistance request form” on the page Contacts of the site www.qem.it. Our technicians will obtain essential elements for understanding your problem. |
Repair
In order to provide you with an efficient service, please read and follow the instructions here reported
Shipping
It is recommended to pack the instrument with materials that can absorb any falls.
 |  |  |
| Use the original packaging: it must protect the instrument during transport. | Attach: 1. A description of the anomaly; 2. Part of the wiring diagram where the instrument is inserted 3. Programming the instrument ( set up, work quotas, parameters …). | A thorough description of the problem will allow us to quickly identify and resolve your problem. Careful packaging will avoid further inconveniences. |